Optimal Foods for Liver Health: A Scientific Perspective
Foods for Liver Health - The liver is an essential organ responsible for a myriad of functions pivotal to maintaining overall health. It plays a crucial role in metabolism, energy production, detoxification, and the regulation of body weight. Therefore, ensuring liver health is paramount for an individual's well-being. Here you can learn about the ideal foods that support liver health, how liver health impacts energy, weight, metabolism, and overall health, and learn why ultra-processed foods and xenobiotics may harm the liver.
How the Health of your Liver Affects Your Daily Life
A healthy liver is essential for maintaining robust daily life activities. A buildup of harmful toxins, especially xenobiotics (manmade toxins found in food, drinks, and our environment), can hinder physical and mental performance. A healthy liver ensures a balanced metabolism, critical for energy production and utilization, allowing us to stay active and alert throughout the day.
The liver plays a significant role in breaking down proteins and managing blood sugar levels. A healthy liver supports muscle function, improves energy levels and so reduces the likelihood of fatigue. Proper liver function also enhances immunity and reduces inflammation, contributing to overall vitality and resilience against illnesses.
A Healthy Liver is Imperative for Overall Function
The liver is imperative for excellent health due to its multifaceted role in the body. It is the primary organ for detoxification, filtering out toxins and waste products from the blood, thus preventing harm to other organs. It also plays a vital part in metabolism by regulating the balance of energy production and storage.
The liver synthesizes proteins essential for blood clotting and produces bile necessary for the digestion and absorption of fats. And it helps maintain hormonal balance, while storing essential vitamins and minerals.
A healthy liver aids in controlling blood sugar levels by converting excess glucose into glycogen for storage. When the liver functions optimally, it enhances immunity, reduces inflammation, and ensures overall vitality. Therefore, nourishing and protecting the liver is crucial for sustaining energy, managing weight, and maintaining optimal health.
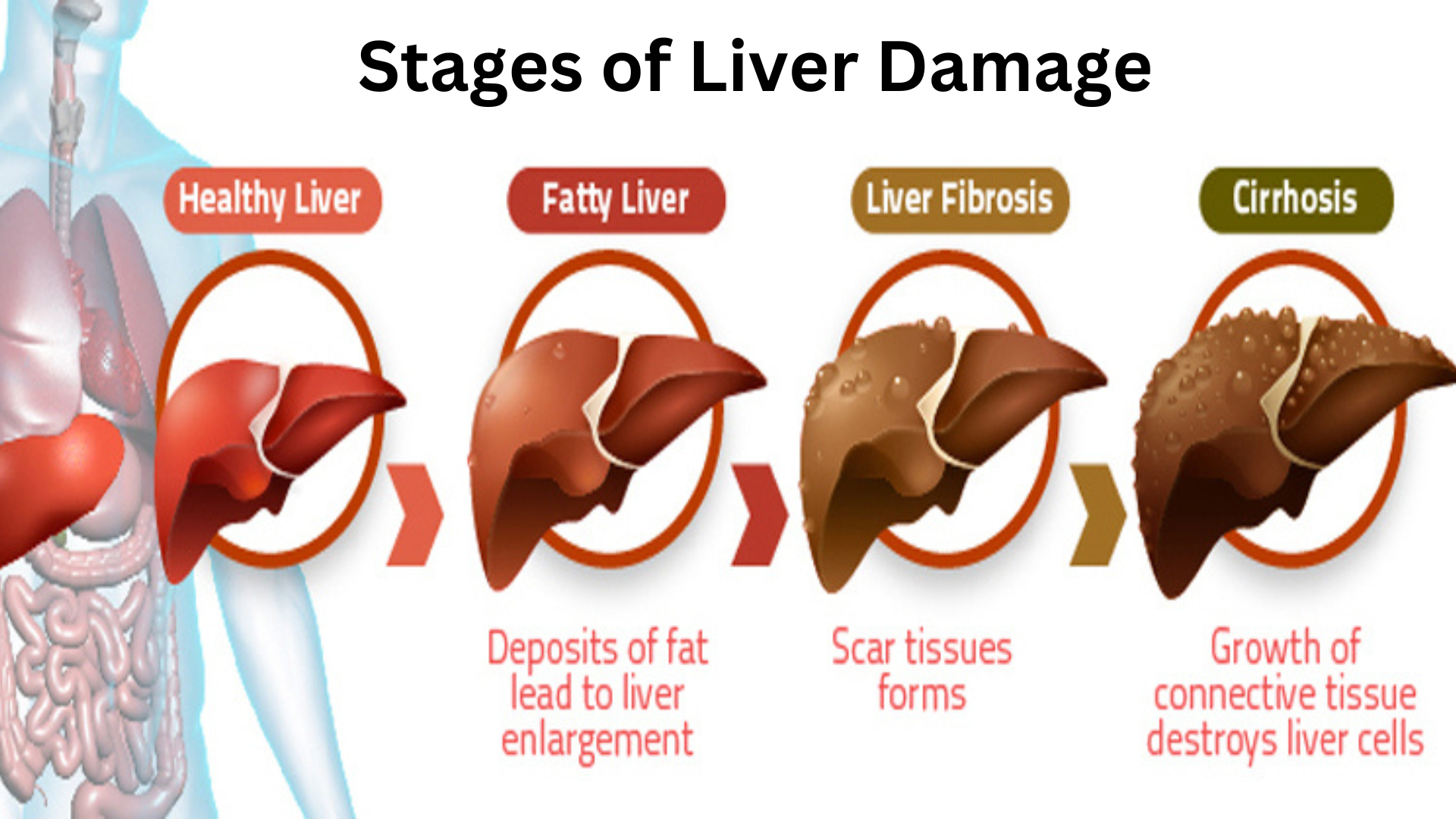
Do I Need Foods for Liver Health
If you're feeling sluggish, have poor digestion, unexplained weight gain or have a difficult time losing weight even when eating healthy, your liver may be overworked.
And overworked liver means it is too busy constantly working to detoxify and neutralize a barrage of harmful toxins. Toxins include xenobiotics in our food (think food preservatives, colorings, or toxic oils) and metabolic toxins that our bodies create. In fact, when the body encounters xenobiotics in the form of foreign chemicals, it is likely to create metabolic toxins as part of the process of metabolism! No wonder so many of us are fatigued or stressed!
Some signs your liver is overworked might include:
General Symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or abdomen
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Bruising easily
- Spider veins
- Digestive Issues
- Pale or clay-colored stools
- Dark urine
- Bloating
- Unexplained weight gain or weight loss
The Harmful Effects of Ultra-Processed Foods and Xenobiotics on the Liver
Ultra-Processed Foods - Ultra-processed foods are often high in sugars, unhealthy fats, and additives, which can harm liver health. These foods can lead to insulin resistance, increasing the risk of NAFLD. Excessive sugar intake, particularly fructose, can cause fat accumulation in the liver and contribute to inflammation. Unhealthy fats, including trans fats and saturated fats, can also impair liver function and promote liver disease.
Xenobiotics - Xenobiotics are foreign substances that the liver must detoxify. These include environmental pollutants, drugs, and chemicals found in food and water. The liver's detoxification processes can be overwhelmed by excessive exposure to xenobiotics, leading to liver damage. Some xenobiotics, such as heavy metals and pesticides, can directly harm liver cells and impair their function.
Mechanisms of Harm
The harmful effects of ultra-processed foods and xenobiotics on the liver can be attributed to several mechanisms:
- Oxidative Stress: Both ultra-processed foods and xenobiotics can increase the production of free radicals, leading to oxidative stress. Oxidative stress damages liver cells and impairs their function, contributing to liver disease.
- Inflammation: Chronic consumption of ultra-processed foods and exposure to xenobiotics can cause inflammation in the liver. Inflammation further damages liver cells and promotes fibrosis, which can lead to cirrhosis.
- Insulin Resistance: Ultra-processed foods, particularly those high in sugars, can cause insulin resistance. Insulin resistance disrupts glucose metabolism and contributes to fat accumulation in the liver, increasing the risk of NAFLD.
Foods That Promote Liver Health
Leafy Greens - Leafy greens such as spinach, kale, and arugula are rich in vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C and antioxidants that help reduce inflammation. They contain glutathione, which aids in the detoxification processes of the liver, protecting it from damage caused by free radicals and toxins.
Cruciferous Vegetables - Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts contain compounds such as indole-3-carbinol and sulforaphane. These compounds support the liver's detoxification enzymes and promote the excretion of harmful substances. Regular consumption of these vegetables has been associated with a reduced risk of liver cancer.
Garlic - Garlic is known for its sulfur-containing compounds, particularly allicin, which activate liver enzymes responsible for flushing out toxins. Additionally, garlic has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which further support liver health.
Fatty Fish - Fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and mackerel are high in omega-3 fatty acids. These healthy fats reduce liver inflammation and prevent the accumulation of fat in the liver, which can lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Omega-3s also improve insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for liver health.
Nuts - Nuts, especially walnuts, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants. They help reduce liver inflammation and oxidative stress. Walnuts also contain arginine, an amino acid that assists in detoxifying ammonia, a toxin produced in the liver.
Berries - Berries such as blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are packed with antioxidants, including polyphenols and anthocyanins. These antioxidants protect the liver from free radical damage and inflammation. Berries also improve glucose metabolism, which is essential for liver health.
Turmeric - Turmeric contains curcumin, a powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant compound. Curcumin enhances bile production, which aids in the digestion and absorption of fats. It also helps in detoxifying the liver and protecting it from damage.
Green Tea - Green tea is rich in catechins, a type of antioxidant that helps protect the liver from oxidative stress and inflammation. Regular consumption of green tea has been shown to prevent fat accumulation in the liver and reduce the risk of liver diseases.
Olive Oil - Extra virgin olive oil is a healthy fat that helps reduce liver enzyme levels and fat accumulation in the liver. It also improves insulin sensitivity and reduces inflammation, promoting overall liver health.
Citrus Fruits - Citrus fruits like oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are high in vitamin C and antioxidants. They boost the liver's detoxification processes and protect it from damage caused by free radicals. Grapefruit, in particular, contains naringenin and naringin, which have been shown to protect the liver from injury.
Avocados - Avocados are rich in healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants. They contain glutathione, which supports the liver's detoxification processes. Avocados also help reduce liver inflammation and improve overall liver function.
Berries such as blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are packed with antioxidants, including polyphenols and anthocyanins. These antioxidants protect the liver from free radical damage and inflammation. Berries also improve glucose metabolism, which is essential for liver health.
Turmeric - Turmeric contains curcumin, a powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant compound. Curcumin enhances bile production, which aids in the digestion and absorption of fats. It also helps in detoxifying the liver and protecting it from damage.
Green Tea - Green tea is rich in catechins, a type of antioxidant that helps protect the liver from oxidative stress and inflammation. Regular consumption of green tea has been shown to prevent fat accumulation in the liver and reduce the risk of liver diseases.
Olive Oil - Extra virgin olive oil is a healthy fat that helps reduce liver enzyme levels and fat accumulation in the liver. It also improves insulin sensitivity and reduces inflammation, promoting overall liver health.
Citrus Fruits - Citrus fruits like oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are high in vitamin C and antioxidants. They boost the liver's detoxification processes and protect it from damage caused by free radicals. Grapefruit, in particular, contains naringenin and naringin, which have been shown to protect the liver from injury.
Avocados - Avocados are rich in healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants. They contain glutathione, which supports the liver's detoxification processes. Avocados also help reduce liver inflammation and improve overall liver function.

Impact of Liver Health on Energy, Weight, Metabolism, and
Health
Energy Production
The liver plays a crucial role in energy production through gluconeogenesis, the process of generating glucose from non-carbohydrate sources. A healthy liver ensures a steady supply of glucose, which is vital for maintaining energy levels. Additionally, the liver stores glycogen, which is converted to glucose when needed, providing the body with a quick source of energy.
Weight Regulation
Liver health is closely linked to weight management. The liver regulates fat metabolism by producing bile, which helps break down fats during digestion. When the liver is functioning optimally, it prevents the accumulation of fat in the body, particularly around the abdomen. Conversely, a compromised liver can lead to conditions like NAFLD, which can contribute to weight gain and obesity.
Metabolism
The liver is central to metabolic processes, including carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism. It converts excess glucose into glycogen for storage and releases it when the body requires energy. The liver also processes amino acids for protein synthesis and breaks down lipids for energy production. A healthy liver ensures efficient metabolism, which is essential for overall health and well-being.
Overall Health
Liver health impacts overall health in several ways. The liver detoxifies harmful substances, including xenobiotics, drugs, and alcohol, preventing them from causing damage to other organs. It produces essential proteins like albumin and clotting factors, which are crucial for maintaining blood health. Furthermore, the liver stores vitamins and minerals, ensuring a steady supply of nutrients necessary for various bodily functions.